Jak zmierzyć napięcie elektryczne i natężenie prądu
Używanie multimetru:
Podczas używania multimetru warto zwrócić uwagę na kilka podstawowych kwestii:
- zakres mierzonej wielkości – należy wybrać zakres większy od spodziewanej wartości pomiaru, jednak najmniejszy z możliwych (wybranie zbyt dużego zakresu skutkować będzie mniejszą dokładnością pomiaru) – np. chcąc zmierzyć napięcie w gniazdku sieciowym o spodziewanej wartości 230V i możliwych zakresach 2, 20, 200, 700 i 1000, najlepszym wyborem będzie zakres 700V – jest najmniejszy spośród zakresów większych od spodziewanej wartości. Przy sprawdzaniu napięcia na baterii 9V najlepszym wyborem będzie zakres 20V, podczas sprawdzania napięcia na baterii 1,5V – zakres 2V.
- rodzaj zmienności mierzonej wartości – podczas mierzenia napięcia lub prądu, niezwykle istotnym elementem jest rodzaj zmienności – mierzenie np. napięcia zmiennego woltomierzem przystosowanym do napięcia stałego skutkować będzie błędnym wynikiem pomiaru. Na różnych multimetrach stosowane są różne oznaczenia:
| Mierzona wielkość i rodzaj zmienności | Oznaczenie symboliczne | Oznaczenie tekstowe |
|---|---|---|
| Napięcie stałe | 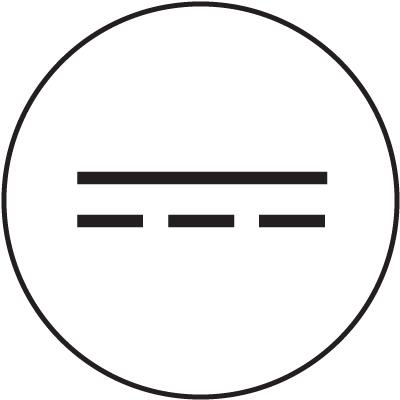 |
DCV |
| Napięcie zmienne | 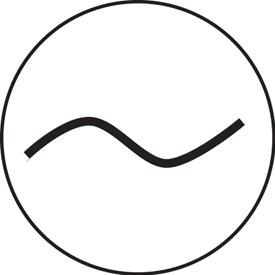 |
ACV |
| Prąd stały |  |
DCA |
| Prąd zmienny |  |
ACA |
Jak zmierzyć napięcie
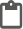
Napięcie mierzy się podłączając woltomierz równolegle do odbiornika:
Jak zmierzyć prąd
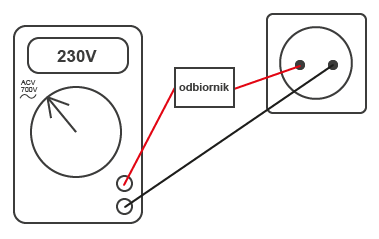
Napięcie mierzy się podłączając amperomierz szeregowo z odbiornikiem (bardzo niska rezystancja wewnętrzna spowodowałaby zwarcie i trwałe uszkodzenie amperomierza przy podłączeniu go równolegle z odbiornikiem):